Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Construct Model 1 with Helper Functions¶
This example demonstrates how to construct a 3D geological model of the Model 1 deposit using GemPy. It leverages custom APIs to streamline the modeling process.
import time
import os
import xarray as xr
from dotenv import dotenv_values
import gempy as gp
import gempy_viewer as gpv
from vector_geology.model_1_builder import initialize_geo_model
from vector_geology.omf_to_gempy import process_file
Start the timer to measure execution time
start_time = time.time()
Load environment variables and path configurations This step is crucial for setting up the directory paths for the model data.
config = dotenv_values()
path = config.get("PATH_TO_MODEL_1_Subsurface")
Initialize lists to store data Here we prepare the containers for the structural elements and the global extent.
structural_elements = []
global_extent = None
color_gen = gp.data.ColorsGenerator()
Process each .nc file in the specified directory This loop reads the necessary data from each .nc file for modeling.
for filename in os.listdir(path):
base, ext = os.path.splitext(filename)
if ext == '.nc':
structural_element, global_extent = process_file(os.path.join(path, filename), global_extent, color_gen)
structural_elements.append(structural_element)
Initialize the GemPy model We use the data processed above to initialize the geological model with GemPy.
geo_model = initialize_geo_model(
structural_elements=structural_elements,
extent=global_extent,
topography=(xr.open_dataset(os.path.join(path, "Topography.nc"))),
load_nuggets=True
)
/home/leguark/gempy/gempy/core/data/structural_frame.py:188: UserWarning: The basement color was already used in the structural elements.Changing the basement color to #015482.
warnings.warn(f"The basement color was already used in the structural elements."
Active grids: GridTypes.NONE|TOPOGRAPHY|DENSE
Display the initialized model It’s helpful to print the model to verify its initialization.
print(geo_model)
{'_interpolation_options': InterpolationOptions(kernel_options={'range': 5, 'c_o': 10, 'uni_degree': 1, 'i_res': 4, 'gi_res': 2, 'number_dimensions': 3, 'kernel_function': <AvailableKernelFunctions.cubic: KernelFunction(base_function=<function cubic_function at 0x7fea8a6cd480>, derivative_div_r=<function cubic_function_p_div_r at 0x7fea8a6cd510>, second_derivative=<function cubic_function_a at 0x7fea8a6cd5a0>, consume_sq_distance=False)>, 'kernel_solver': <Solvers.DEFAULT: 1>, 'compute_condition_number': False, 'optimizing_condition_number': False, 'condition_number': None}, evaluation_options={'_number_octree_levels': 5, '_number_octree_levels_surface': 4, 'curvature_threshold': -1, 'error_threshold': 1.5, 'min_octree_level': 2, 'mesh_extraction': True, 'mesh_extraction_masking_options': <MeshExtractionMaskingOptions.INTERSECT: 3>, 'mesh_extraction_fancy': True, 'evaluation_chunk_size': 5000000, 'compute_scalar_gradient': False, 'verbose': False}, temp_interpolation_values=<gempy_engine.core.data.options.temp_interpolation_values.TempInterpolationValues object at 0x7fea2d6872e0>, debug=True, cache_mode=CacheMode.IN_MEMORY_CACHE, cache_model_name=, block_solutions_type=BlockSolutionType.OCTREE, sigmoid_slope=50000, debug_water_tight=False),
'grid': Grid(_octree_grid=None,
_dense_grid=RegularGrid(resolution=array([20, 10, 20]),
extent=array([ 5.59902830e+05, 5.64955682e+05, 6.44278260e+05, 6.50608735e+05,
-1.75340000e+03, 1.60326604e+02]),
values=array([[ 5.60029151e+05, 6.44594784e+05, -1.70555683e+03],
[ 5.60029151e+05, 6.44594784e+05, -1.60987050e+03],
[ 5.60029151e+05, 6.44594784e+05, -1.51418417e+03],
...,
[ 5.64829361e+05, 6.50292212e+05, -7.88892213e+01],
[ 5.64829361e+05, 6.50292212e+05, 1.67971089e+01],
[ 5.64829361e+05, 6.50292212e+05, 1.12483439e+02]]),
mask_topo=array([], shape=(0, 3), dtype=bool),
_transform=None),
_custom_grid=None,
_topography=<gempy.core.data.grid_modules.topography.Topography object at 0x7fea789b5600>,
_sections=None,
_centered_grid=None,
values=array([[ 5.60029151e+05, 6.44594784e+05, -1.70555683e+03],
[ 5.60029151e+05, 6.44594784e+05, -1.60987050e+03],
[ 5.60029151e+05, 6.44594784e+05, -1.51418417e+03],
...,
[ 5.64955682e+05, 6.49201963e+05, 1.06993262e+02],
[ 5.64955682e+05, 6.49905349e+05, 8.89864414e+01],
[ 5.64955682e+05, 6.50608735e+05, 7.05702308e+01]]),
length=array([], dtype=float64),
_transform=None,
_octree_levels=-1),
'input_transform': {'_cached_pivot': None,
'_is_default_transform': False,
'position': array([-562422.65655014, -647329.31794742, 823.58712106]),
'rotation': array([0., 0., 0.]),
'scale': array([8.55363115e-05, 8.55363115e-05, 8.55363115e-05])},
'meta': GeoModelMeta(name='Tutorial_ch1_1_Basics',
creation_date=None,
last_modification_date=None,
owner=None),
'structural_frame': StructuralFrame(
structural_groups=[
StructuralGroup(
name=Blue,
structural_relation=StackRelationType.ERODE,
elements=[
Element(
name=HBL,
color=#ffbe00,
is_active=True
),
Element(
name=KKR,
color=#A46283,
is_active=True
)
]
),
StructuralGroup(
name=Red,
structural_relation=StackRelationType.ERODE,
elements=[
Element(
name=ABL,
color=#1D3943,
is_active=True
),
Element(
name=LGR,
color=#6394A4,
is_active=True
),
Element(
name=WAL,
color=#72A473,
is_active=True
)
]
)
],
fault_relations=
[[False, False],
[False, False]],
}
Modify the interpolation options This step configures the model’s interpolation settings for better accuracy.
interpolation_options = geo_model.interpolation_options
interpolation_options.mesh_extraction = True
interpolation_options.kernel_options.range = 0.7
interpolation_options.kernel_options.c_o = 3
interpolation_options.kernel_options.compute_condition_number = True
Modify surface points Adjustments to the surface points can influence the resulting geological features.
gp.modify_surface_points(
geo_model,
slice=0,
X=geo_model.surface_points_copy.data[0][0] + 130,
)
Compute the model This is where the model computation happens, utilizing the GemPy engine.
before_compute_time = time.time()
gp.compute_model(
geo_model,
engine_config=gp.data.GemPyEngineConfig(
backend=gp.data.AvailableBackends.PYTORCH,
dtype="float32"
),
)
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.PYTORCH
Condition number: 146825.828125.
Condition number: 276737.5.
Plot 2D model visualization Visualizing the model in 2D helps in understanding the geological layers.
gpv.plot_2d(geo_model, show_scalar=False)
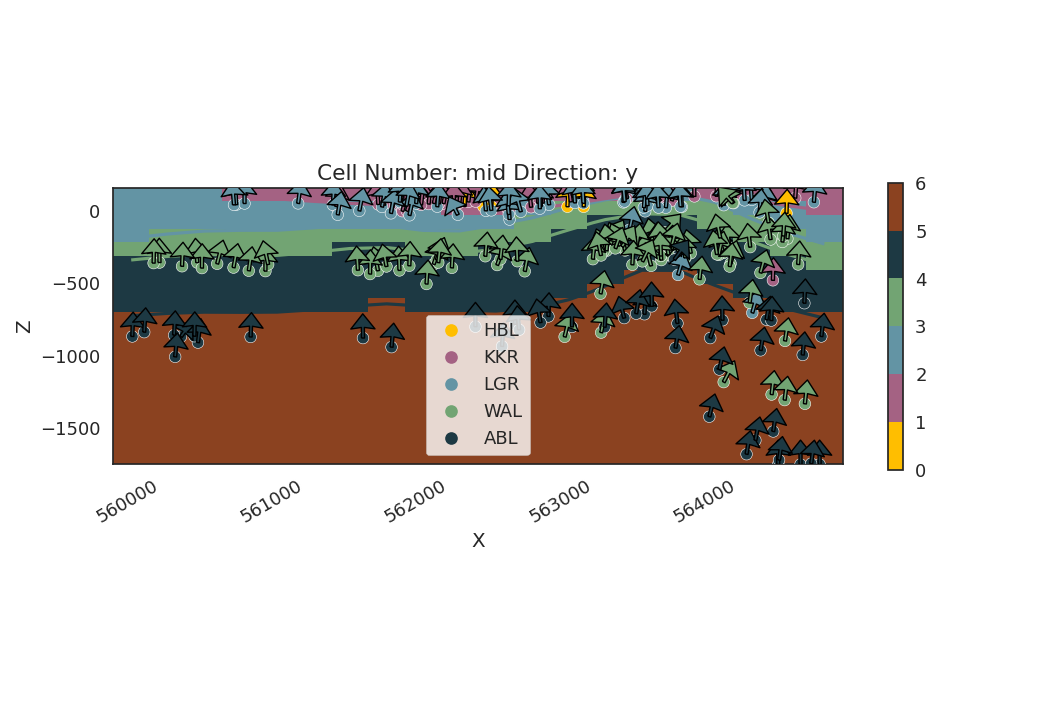
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_2d.visualization_2d.Plot2D object at 0x7fea2d483790>
3D visualization with gempy_viewer A 3D view provides a comprehensive look at the model’s structure.
gempy_vista = gpv.plot_3d(
model=geo_model,
show=True,
kwargs_plot_structured_grid={'opacity': 0.8}
)
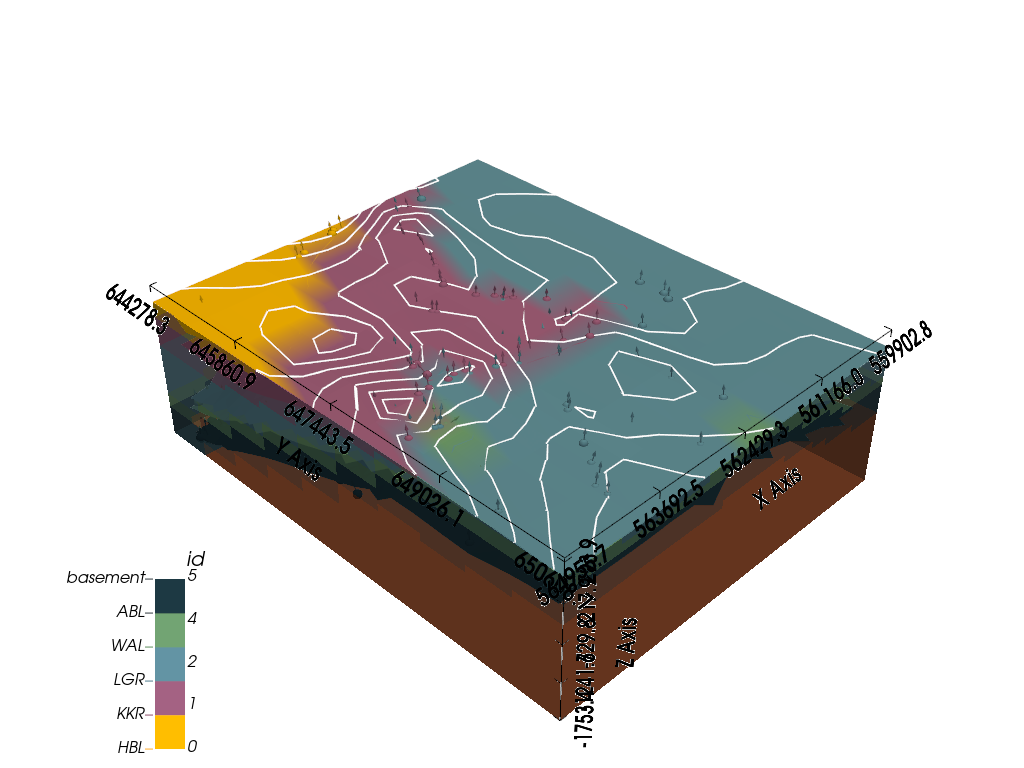
Calculate and print execution times It’s useful to know how long different parts of the process take.
end_time = time.time()
prep_time = before_compute_time - start_time
compute_time = end_time - before_compute_time
execution_time = end_time - start_time
print(f"Preparation time: {prep_time} seconds.")
print(f"Computation time: {compute_time} seconds.")
print(f"Total execution time: {execution_time} seconds.")
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = -2
Preparation time: 1.0133297443389893 seconds.
Computation time: 4.729570627212524 seconds.
Total execution time: 5.742900371551514 seconds.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.802 seconds)
